Thermoset Composite Material & its Moulding Technique
Composites are defined as “a combination of plastic resin and fibre reinforcement.” Another term for composites is used in the past is reinforced plastics.
Sheet Moulding Compound : Sheet moulding compound (SMC) or sheet moulding composite is a ready to mould glass fibre reinforced polyester material primarily used in compression moulding.[1] The sheet is provided in rolls weighing up to 100 kg. Alternatively, the resin and related materials may be mixed on site when a producer wants greater control over the chemistry and filler.
Process : Sheet Moulding Compound (SMC) is a compression moulding compound often used for larger parts where higher mechanical strength is needed. SMC is a fibre reinforced thermoset material. Glass reinforcement is between 10% and 50%, and glass length is slightly longer than Dough Moulding Compound (DMC) - between 1/2-inch and 1-inch (25mm).
Thermoset Sheet Moulding Compound (SMC) is a mixture of polymer resin, inert fillers, fiber reinforcement, catalysts, pigments and stabilizers, release agents, and thickeners and possesses strong dielectric properties. Manufacture of sheet moulding compounds is a continuous in-line process. The material is sheathed both top and bottom with a polyethylene or nylon plastic film to prevent autoadhesion. The paste is spread uniformly onto the bottom film. Chopped glass fibers are randomly deposited onto the paste. The top film is introduced and the sandwich is rolled into a pre-determined thickness.
The sheet is allowed to mature for 48 hours. Sheet moulding compounds can be moulded into complex shapes. Superior mechanical properties and surface appearance, plus excellent electrical insulation make this thermoset material ideal for automotive Class A body panels, high-strength electrical parts, business equipment cabinets, personal watercraft, and various structural components.
Dough Moulding Compound
Dough Moulding Compound (DMC) is a thermoset plastic resin blend of various inert fillers, fiber reinforcement, catalysts, stabilizers, and pigments that form a viscous, 'puttylike' moulding compound. DMC is highly filled and reinforced with short fibers. Glass reinforcement represents between 10% and 30%, with glass length typically between 6mm to 12mm. Depending on the end-use application, dough moulding compounds are formulated to achieve close dimensional control, flame and track resistance, electrical insulation, corrosion and stain resistance, superior mechanical properties, low shrink, and colour stability. Its excellent flow characteristics, dielectric properties, and flame resistance make this thermoset material wellsuited to a wide variety of applications requiring precision in detail and dimensions as well as high performance.
Process
Basic raw materials are resins, additives, catalysts, mould release agents and fillers. For coloured compounds, a pigment is added to the paste. The paste is then mixed with fibres, usually glass fibres. Bulk Moulding Compound (BMC) is prepared in a mixer. After preparing a base paste it will be loaded into the mixing device. Then all other ingredients are added and homogenized. The compound is packed into bags until moulding. To avoid any material changes during storage and transport it is packaged in a styrene tight packaging.
Process Used for Moulding SMC & DMC Composite Materials
Compression Moulding require following components:
1. Component raw materials SMC is available in Sheet form; DMC is available in dough form & Metal inserts if required
2. Mould with desired shaped cavity
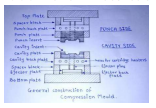
3. Moulding Machine The machine is the fundamental element of this process. A compression moulding machine is like a power press except power press have a fast operation and do not stay for more time at stroke. CM machines stay for a predetermined time when actuated. It is more like a UTM machine. According to the shape and volume of the finished product, machine tonnage is decided. We have machines from 25 ton to 500 ton.
4. Process Flow
- Heating the Mould (temperature 165 deg C maximum)
- Placing the material in the cavity & close the mould
- Curing Reaction depends on the shape & volume of the raw material.
- Mould opening & Ejection.
- Cleaning the Mould for next operation.
- Post moulding operation for deflashing.
- Quality check of moulded products
- Packing and dispatch